Half inch plywood is a versatile material widely used in construction and woodworking. According to the APA – The Engineered Wood Association, plywood, including half inch varieties, accounts for over 40% of the structural panel market in North America. This figure highlights its importance in various applications ranging from residential to commercial projects.
Half inch plywood is often used for wall sheathing and flooring. It provides strength and stability in construction. Its lightweight nature makes it easy to handle, yet it maintains durability against wear and tear. Yet, not all uses are ideal. Some projects may benefit from thicker panels, which can offer more support.
Interestingly, preferences for half inch plywood vary among builders. Some prefer it for cabinetry, while others see limitations. It’s essential to assess the specific needs of a project. Misjudging these requirements can lead to structural issues down the line. Therefore, while half inch plywood has its advantages, thoughtful consideration is crucial.
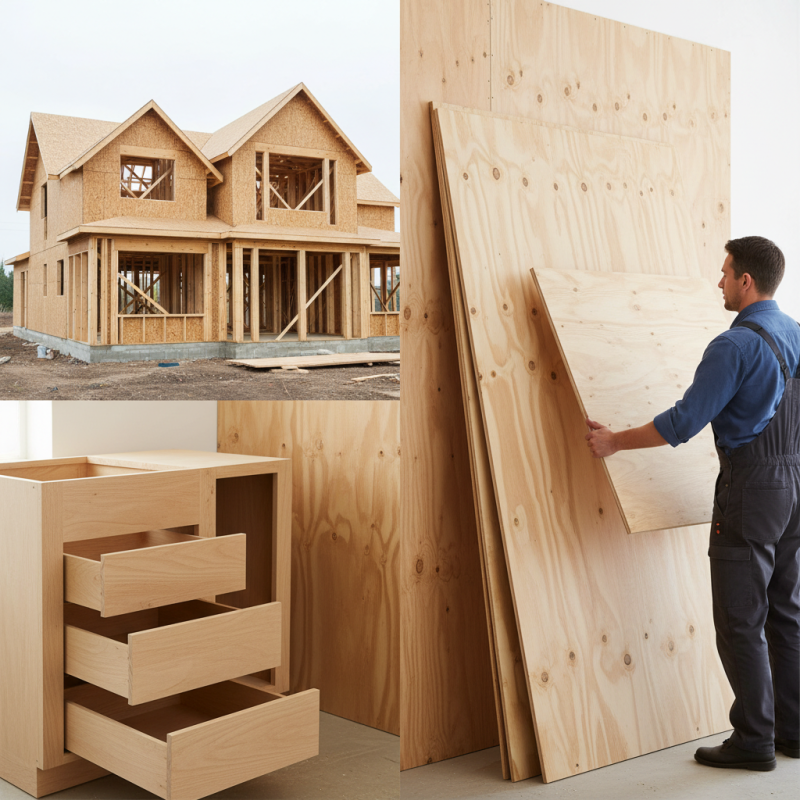

Half inch plywood is a versatile material found in many construction projects.
It serves various purposes, making it an essential choice for builders. Commonly, this thickness is used for
wall sheathing. It provides stability and insulation,
crucial for any structure. Contractors often rely on it for subfloors, ensuring a
solid base for flooring materials.
In home renovations, half inch plywood is frequently utilized for cabinetry and furniture.
It offers a great balance between strength and weight.
However, not all plywood is created equal. Some may warp or delaminate under moisture.
It's essential to choose wisely for your specific needs. Additionally, while it can be cost-effective, rushing
the decision might lead to regrets later. Evaluating quality and purpose is vital in making the
right choice for your project.
Half inch plywood has become a popular choice in furniture making due to its versatility and strength. This thickness is ideal for various applications, from cabinetry to shelving. It provides the right balance between weight and durability. According to industry reports, half inch plywood can support heavy loads, making it a dependable material for both structural and aesthetic purposes.
One major advantage of half inch plywood is its ease of handling. It is lightweight compared to thicker alternatives. Carpenters often find it easier to cut, shape, and join. A report by the Wood Products Association indicates that using half inch plywood can save up to 20% in labor costs due to its manageable size. This makes it a cost-effective option, especially for mass production.
While half inch plywood has many benefits, it is essential to address potential downsides. Its thinner profile may not be suitable for every application. Some furniture designs require thicker materials for additional strength. Additionally, the quality of plywood can vary. It's critical to choose high-quality options to avoid warping or splitting. This requires careful sourcing and consideration.
| Application | Advantages | Typical Thickness |
|---|---|---|
| Cabinetry | Durable and cost-effective | 1/2 inch |
| Furniture Frames | Lightweight yet strong | 1/2 inch |
| Decorative Panels | Versatile design options | 1/2 inch |
| Shelving | Supports considerable weight | 1/2 inch |
| Wall Paneling | Easy to install and finish | 1/2 inch |

Half inch plywood plays a crucial role in cabinetry design and durability. This thickness is often preferred for cabinet carcasses and shelving due to its balance of weight and strength. According to industry reports, plywood of this size shows a shear strength of approximately 1,300 PSI, making it a reliable choice for various cabinetry applications.
However, not every half inch plywood is created equal. Variability exists in the quality of wood used. This can affect the durability and aesthetics of the final product. For instance, some may warp or delaminate over time. A survey from the National Wood Furniture Association indicates that nearly 25% of cabinetry failures are attributed to poor plywood quality. This highlights the importance of selecting higher-grade materials for long-lasting designs.
Design aspects also matter. Many designers appreciate the uniformity of half inch plywood, which allows for clean lines and modern aesthetics. Yet, some find it lacks the heft desired in certain styles. It's essential to reflect on how this choice impacts both functionality and visual appeal. Balancing cost with quality and design is a delicate task that deserves careful thought.
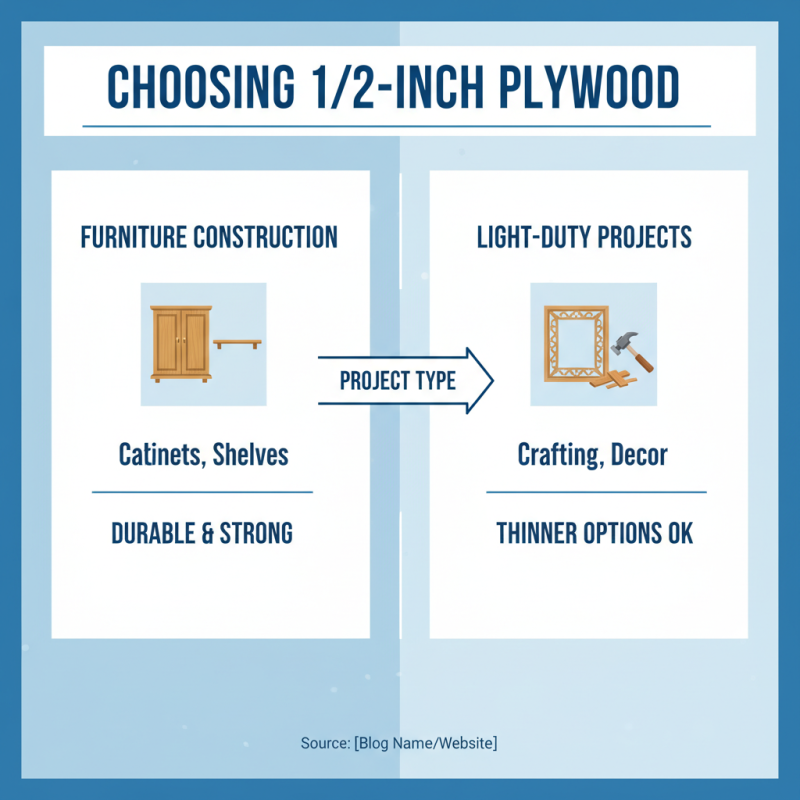
When choosing half-inch plywood, several factors come into play. The type of project significantly influences your selection. For furniture construction, half-inch plywood offers durability and strength. It works well for building cabinets or shelves. In contrast, if you’re working on light-duty applications, like decorative projects or crafting, thinner options may suffice.
Consider the wood source. Plywood can come from various woods, each with unique characteristics. Birch, for instance, is sturdy and easy to finish. Meanwhile, softer woods like pine may be cheaper but could warp. Assess your project's needs and choose accordingly.
Tips: Always check the number of layers. Quality plywood usually has more plies. This increases stability and prevents warping. Look for voids; they can compromise the wood’s integrity. If imperfections seem excessive, rethink your choice. Remember, using subpar materials may save money now but could lead to regrets later. Invest wisely in plywood that suits your specific needs.
When considering alternatives to half-inch plywood for various projects, several options stand out. For example, oriented strand board (OSB) can perform similarly to plywood. Researchers indicate that OSB can be more cost-effective, often reducing project budgets by about 20%. However, durability may not match that of half-inch plywood in demanding conditions.
Another alternative is medium-density fiberboard (MDF). It excels in applications requiring smooth surfaces for painting. MDF is denser than plywood, making it ideal for furniture and cabinetry. However, it lacks moisture resistance. Data suggests that MDF can swell when exposed to excessive humidity, leading to potential project failures.
Finally, particle board can be useful for low-stress applications. Reports show that particle board can handle light loads well but isn't as robust as plywood or MDF. This material is often underappreciated for its affordability and versatility, yet it requires careful handling. Most projects using particle board may face challenges in long-term durability and aesthetic appeal. The choice of material ultimately reflects project needs and budget constraints.





Signup our newsletter to get update information, promotion or insight.